UPSC Key: Sarkaria Commission, Kavach 5.0, and auto component industry
Why is the Supreme Court prescribing a deadline to the President on bills referred by the Governor relevant to the UPSC exam? What is the significance of topics such as the integration of the auto component industry into global value chains, Article 201, and AI-enabled maker lab have on both the preliminary and main exams? You can learn more by reading the Indian Express UPSC Key for April 12, 2025.
 UPSC Key April 2025: Here's what you should be reading from the April 12, 2025 edition of The Indian Express
UPSC Key April 2025: Here's what you should be reading from the April 12, 2025 edition of The Indian ExpressImportant topics and their relevance in UPSC CSE exam for April 12, 2025. If you missed the April 11, 2025, UPSC CSE exam key from the Indian Express, read it here.
FRONT
In a first, Supreme Court sets 3-month deadline for President to decide on Bills referred by Governor
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues
Mains Examination: General Studies-II: Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein
What’s the ongoing story: In setting timelines for Governors to act on Bills presented to them by the state legislatures, the Supreme Court has, for the first time, prescribed that the President should take a decision on the Bills reserved for consideration by the Governor within a period of three months from the date on which such reference is received.
Key Points to Ponder:
— What are the major outcomes of the Supreme Court in the TN governor case?
— What are Articles 200 and Article 201?
— Why did the Supreme Court set a timeline for the President to take a decision on the Bills reserved for consideration by the Governor?
— What are pocket veto and absolute veto?
— What are the various issues of conflict between Centre-state relations?
— What is the role of the Governor?
— What are the issues regarding the ordinance power of the Governor and President?
— Read about the Sarkari Commission recommendation and Punchhi Commission recommendation on the role of the governor
Key Takeaways:
— Calling for a decision within three months is significant because under Article 201 of the Constitution, no timeframe has been set for a Presidential decision.
— It said “where the Governor reserves a Bill for the consideration of the President and the President in turn withholds assent thereto then, it shall be open to the State Government to assail such an action before this Court”.
— Writing for the bench, Justice Pardiwala noted that under Article 201, the President has two options once a Bill is reserved by the Governor for his/her consideration – grant or withhold assent.
— The bench said “one of the features of Article 201 which have been the cause of differences in Centre-State relations over the years” is the absence of a time-limit within which the President is required to declare the grant or withholding of assent once the Bill is reserved for his/her consideration by the Governor.
— It said the Sarkaria Commission had pointed to this and “recommended that definite timelines must be adopted for facilitating the efficient disposal of references under Article 201” and that “the reading of a timeline in Article 201 was also suggested by the Punchhi Commission”.
— The Sarkaria Commission, headed by former Supreme Court judge Justice R S Sarkaria, was set up in 1983 to review the working of the existing arrangements between the Union and the States. The Punchhi Commission too was on Centre- State relations and was set up in 2007 under former Chief Justice of India Justice M M Punchhi.
— The ruling said “although we are cognisant of the fact that in discharge of his powers under Article 201, the President is expected to ‘consider’ the Bill and such ‘consideration’ may be difficult to be bound by strict timelines, yet it cannot be a ground to justify inaction on part of the President”.
Do You Know:
— In a significant decision, a bench of Justices J B Pardiwala and R Mahadevan of the Supreme Court declared the action of Tamil Nadu Governor R N Ravi in reserving 10 Bills for the consideration of the President in November last year after their due reconsideration by the state Assembly as erroneous and illegal.
— While laying down the timeline for Governors to decide on Bills, the Supreme Court referred to Article 200 of the Constitution. Article 200 specifically deals with the issue of granting assent to Bills. When a Bill passed by the legislature of a state is presented to the Governor, the Governor has four options: (1) grant assent to the Bill; (2) withhold assent to the Bills; (3) return the Bills for reconsideration; or (4) reserve the Bill for the consideration of the President.
— The key difference between the governor and the president is in the manner of appointment and removal — whereas the president is elected by the elected representatives of the country, the governor is appointed by the Union government alone. Whereas the president can only be removed by way of impeachment, the governor can be removed from office at the pleasure of the Union government.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Knowledge Nugget: SC Verdict on TN Governor — Why it matters for UPSC
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
(1) Which one of the following suggested that the Governor should be an eminent person from outside the State and should be a detached figure without intense political links or should not have taken part in politics in the recent past? (2019)
(a) First Administrative Reforms Commission (1966)
(b) Rajamannar Committee (1969)
(c) Sarkaria Commission (1983)
(d) National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2000)
(2) Which one of the following statements is correct? (2013)
(a) In India, the same person cannot be appointed as Governor for two or more States at the same time
(b) The Judges of the High Court of the States in India are appointed by the Governor of the State just as the Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President
(c) No procedure has been laid down in the Constitution of India for the removal of a Governor from his/her post
(d) In the case of a Union Territory having a legislative setup, the Chief Minister is appointed by the Lt. Governor on the basis of majority support
Previous year UPSC Mains Question Covering similar theme:
Discuss the essentials of the 69th Constitutional Amendment Act and anomalies, if any that have led to recent reported conflicts between the elected representatives and the institution of the Lieutenant Governor in the administration of Delhi. Do you think that this will give rise to a new trend in the functioning of the Indian federal politics? (2016)
EXPRESS NETWORK
Ashwini Vaishnaw announces Kavach 5.0 system to increase Mumbai local services by 30%
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: General Studies-III: Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
What’s the ongoing story: In a major step to upgrade Mumbai’s suburban train travel, Union Minister for Railways Ashwini Vaishnaw on Friday announced that Kavach 5.0, the latest in the series of Automatic Train Protection (ATP) systems, will be implemented to increase the number of trains by 30 percent. Currently, Kavach 4.0 version is under implementation in the different parts of Indian Railways.
Key Points to Ponder:
— What are Automatic Train Protection (ATP) systems?
— What is the difference between Kavach 4.0 and Kavach 5.0?
— Due to Kavach 5.0, we will be able to add 30 percent more trains. How?
— What are the basic features of Kavach?
— What are the problems facing the railway sector in India?
— What are the reasons for frequent trail accidents? How can it be avoided?
— What are the recommendations of the Debroy Committee on Railway Reforms?
Key Takeaways:
— Kavach aids the Loco Pilot in running of trains within specified speed limits by automatic application of brakes in case Loco Pilot fails to do so and also helps trains to run safely during inclement weather.
— Vaishnaw said that to address demands of improvement in the Mumbai local, better infrastructure, better technology and better trains are required and Indian Railways is working on it.
Do You Know:
— Kavach is India’s very own advanced Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation in collaboration with the Indian industry to prevent train collisions by automatically activating the braking system of the train.
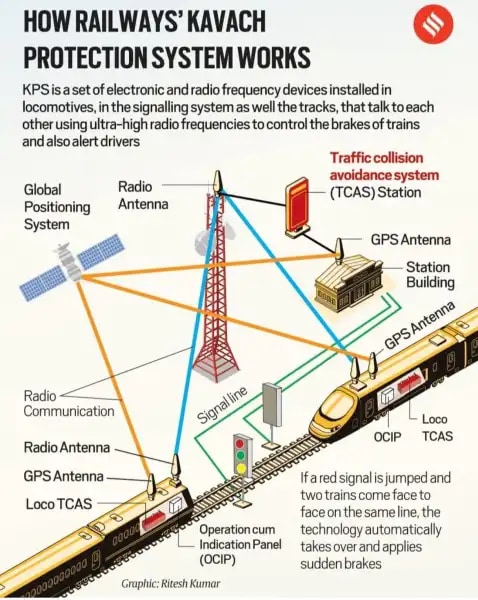
— This technology features an electronic device linked with radio frequency identification systems positioned at stations, trains and tracks. If a loco pilot inadvertently skips a red signal, Kavach automatically activates and controls the train’s braking systems. Additionally, the system detects any trains approaching the same tracks, taking necessary actions to avert collisions and alerting the loco pilot.
— Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS) or Kavach includes the key elements from already existing, and tried and tested systems like the European Train Protection and Warning System, and the indigenous Anti Collison Device.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Knowledge nugget of the day: KAVACH
📍Amrit Bharat 2.0, train to Kashmir, Kavach to be among highlights for Railways in Budget
Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
(3) The Debroy Committee was constituted for
(a) to provide recommendations of MSMEs
(b) Suggest measures for tribal assimilation
(c) Look into the power shortage issue in the textile industry
(d) Recommend measures for reform in railways
UPSC Mains Question Covering similar theme:
The setting up of a Rail Tariff Authority to regulate fares will subject the cash strapped Indian Railways to demand subsidy for obligation to operate nonprofitable routes and services. Taking into account the experience in the power sector, discuss if the proposed reform is expected to benefit the consumers, the Indian Railways or the private container operators. (2014)
THE EDITORIAL PAGE
A second 1991 moment
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: General Studies-III: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation, of resources, growth, development and employment
What’s the ongoing story: Surjit S Bhalla writes: Anyone who claims they know what is happening and what is going to happen with Trump Tariffs (TT) is __ (fill in). But we must all attempt to make sense of the new order unleashed by TT.
Key Points to Ponder:
— What is the economic conflict between China and America?
— How does it impact India?
— What are the economic areas of reform that India needs to implement in the current scenario?
— How did China move ahead of India?
Key Takeaways:
— My suspicion/belief since TT’s opening show on April 2 — when the so-called reciprocal tariffs were announced — is that TT, reciprocal or otherwise, had precious little to do with economic logic or with balancing US trade deficits. They had everything to do with the political economy, that is, China’s long game.
— Then came April 2, “Liberation Day” (liberation from what, one might legitimately ask!), and mighty tariffs were announced for all countries — allies and foes, and even those with just penguins. It was only on April 9 that the anti-China focus of the tariffs became obvious. That is the day when the US policy of containing China became exposed. Ten per cent tariffs for all, and 125 per cent for China.
— The Western world needs India as a counterweight to the Chinese dragon. South Asia is the only region with a labour supply that is expanding, albeit at a decelerating rate. This is the demographic dividend, and it will last at least another decade. Pakistan and Bangladesh will take some time to join.
— India now has the educated and AI-capable workforce to (nearly) match China. It is just a matter of a few years before India’s educated prime-age (25-54 years) labour force exceeds that of China. Never before have India’s economic stars looked so bright. China knows it and the West knows it. Does India know it?
— The choice for India is clear. To keep comfortably growing at 6.2 per cent or accelerate GDP growth to the range of 7.5-8.5 per cent (given normal world conditions) by opening up on trade and FDI and ensuring deep deregulation. It is comfort that kills reform, and indeed induces anti-reform.
Do You Know:
— India’s strategy of initiating talks for a bilateral trade agreement (BTA) with the US, along with its restraint in not retaliating against US tariffs, appears to have paid off, as US President Donald Trump Wednesday paused reciprocal tariffs on 75 countries, including India, while imposing a steep 125 per cent tariff on China in response to its retaliatory measures.
— As the US is India’s largest trading partner, with bilateral trade in 2023 crossing $117 billion. India is also vulnerable to changes in American trade policy, as the US market is India’s largest export market for both goods and services. Most importantly, the US is the only country with which India has a trade surplus, making it a crucial source of US dollar earnings. In this context, the tariff policy of the US also affects the Indian economy on multiple fronts.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍India needs accelerated reforms to reach high income status by 2047: World Bank report
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
(4) Consider the following statements: (UPSC CSE 2022)
1. Tight monetary policy of the US Federal Reserve could lead to capital flight.
2. Capital flight may increase cost of firms with existing External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
3. Devaluation of domestic currency decreases the currency risk associated with ECBs
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
THE IDEAS PAGE
The right way to study AI
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: General Studies-III: Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life.
What’s the ongoing story: Aditya Vishwanath and Chintan Vaishnav wrote: Across history, the most enduring lessons have not been absorbed through passive reading but through doing, tinkering, and experimenting. Whether it’s learning to cook, weave, engineer, or even getting enlightened, active participation (simply “doing”) shapes not just skills, but cognition itself. AI is no exception.
Key Points to Ponder:
— What is the purpose of the “AI-enabled maker lab”?
— What is Atal Innovation Mission (AIM)?
— What is the issue of equitable access in AI learning? How to deal with it?
— What is the significance of experimental learning?
— What are artificial intelligence and machine learning?
— What is the government’s plan for integrating AI and ML? What are the challenges?
Key Takeaways:
— The concept of learning by doing — a foundational principle in education — has long been supported by cognitive science. It’s what psychologist John Dewey championed as experiential learning — where students don’t just know concepts, but apply them, internalise them, and evolve their thinking. This is why we argue that the rise of an “AI-enabled maker lab” is critical (and practical).
— Much like computer labs introduced students to programming, AI maker labs can serve as hands-on spaces for experimenting. These labs allow students to interact with AI tools, see them in action, and test their own models, turning abstract AI principles into concrete experiences.
— The shift is profound — from passive learning to engaged, inquisitive problem-solving. This approach does two critical things. One, it makes AI tangible. Rather than viewing it as an abstract black box, students see AI’s mechanics, biases, and limitations first-hand. Two, it prepares students for AI-driven careers. Students who learn by tinkering don’t just understand AI — they can apply it creatively and fearlessly to solve real-world challenges.
— India has already made significant investments in makerspace infrastructure, particularly through initiatives like the Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) under the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM). With over 10,000 labs operational and plans for thousands more, this network offers a strong starting point to integrate AI literacy through making. But as anyone who has worked closely with these labs knows, infrastructure alone is not enough.
— Integrating AI maker labs into India’s education system must go beyond a top-down deployment of hardware or one-off training modules. With a technology that has challenged the world to think about how we will work and live, interventions must include a serious investment in teacher capacity, school leadership, and local ecosystems .
Do You Know:
— Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is Government of India’s flagship initiative to create and promote a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship across the length and breadth of our country.
— AIM’s objective is to develop new programmes and policies for fostering innovation in different sectors of the economy, provide platforms and collaboration opportunities for different stakeholders, and create an umbrella structure to oversee the innovation & entrepreneurship ecosystem of the country.
— Atal Innovation Mission is establishing Atal Tinkering Laboratories (ATLs) in schools across India. The objective of this scheme is to foster curiosity, creativity, and imagination in young minds; and inculcate skills such as design mindset, computational thinking, adaptive learning, physical computing etc.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍AI basics: What are artificial intelligence and machine learning?
📍UPSC Issue at a Glance | DeepSeek breakthrough: 4 Key Questions You Must Know for Prelims and Mains
UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
(5) With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (UPSC CSE 2020)
1. Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
2. Create meaningful short stories and songs
3. Disease diagnosis
4. Text-to-Speech Conversion
5. Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
ECONOMY
How US, EU FTAs can help integrate auto component sector into global value chains: Niti Aayog report explains
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: General Studies-III: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation, of resources, growth, development and employment
What’s the ongoing story: Free trade agreements (FTAs) with the US and the EU, along with the creation of a conducive environment for foreign joint ventures (JVs), will help integrate India’s burgeoning auto component industry into global value chains, a new NITI Aayog report said on Friday.
Key Points to Ponder:
— What is FTA?
— What is the status of India’s FTA with the US and the EU?
— What is the potential of India’s auto component exports?
— What are the challenges facing this sector in comparison to China?
— What are the challenges in the integration of auto component industry into global value chains?
— Everybody outside of China is looking at India right now. Analyze in terms of global supply chain.
— Learn about the objective of introducing the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme
Key Takeaways:
— It also recommended a fresh Production Support Scheme to partly cover operational and capital expenditure for auto components left out of the ongoing Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme – primarily engines, its components, transmission gears and axles, as well as equipment such as tools and dyes.
— By pursuing a combination of fiscal and non-fiscal incentives outlined in the report, NITI Aayog expects India’s auto component exports to triple to $60 billion by 2030, with the country’s share in global value chains rising from 3 to 8 per cent.
— Stressing the importance of FTAs in boosting export competitiveness, NITI Aayog Member Arvind Virmani said such agreements could also increase investment flows into India and facilitate the creation of foreign JVs.
— India is currently negotiating a bilateral trade deal with Washington and an FTA with Brussels. The report noted that “strategically negotiated” FTAs can encourage foreign investment, technology transfer, and innovation.
— Highlighting India’s potential to attract foreign JVs, NITI Aayog CEO BVR Subrahmanyam said, “Everybody outside of China is looking at India right now.”
— The report proposed a new scheme to develop brownfield auto clusters into global manufacturing hubs. “There is also a need to undertake a thorough audit of existing auto clusters to evaluate utilization, implementation problems, and the state of facilities provided,” it said.
The eight auto clusters identified in the report are: Delhi-NCR, Pune, Sri City, Chennai, Ludhiana, Pithampur, Rajkot, and Sambhaji Nagar.
— The report found that India’s auto component sector faces a 10 per cent cost disadvantage over China, plus an additional 20 per cent differential on manufacturing equipment.
— As a solution, it proposes opex incentives for producing engine cylinders and cylinder heads, pistons and engine valves, crankshafts and camshafts, and transmission gears and axles, along with capex incentives for tools and dyes.
— Despite being the world’s fourth-largest automobile producer after China, US, and Japan, India accounts for just 3 per cent (around $20 billion) of global auto component trade.
Do You Know:
— India’s automotive industry is reflective of the country’s aspirations and is future-ready, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said at the inauguration of Bharat Mobility Global Expo 2025.
— Modi said India is currently the world’s fifth largest economy and its passenger vehicle market is the third largest. “Imagine where our auto market will be when we will be among the top 3 economies. There are many factors driving India’s mobility future, like its big youth population, the growing share of its middle class, rapid urbanisation, and modern infrastructure,” he said.
— Modi also emphasised the ‘Seven Cs’ of his mobility vision – common, connected, convenient, congestion-free, charged, clean, and cutting-edge – and backed green mobility solutions like electric vehicles (EVs), hydrogen fuel, and biofuels.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
Previous year UPSC Mains Question Covering similar theme:
Account for the failure of manufacturing sector in achieving the goal of labour-intensive exports rather than capital-intensive exports. Suggest measures for more labour-intensive rather than capital-intensive exports.(2017)
EXPLAINED
Why confidence in US$ is flagging
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: General Studies-III: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation, of resources, growth, development and employment.
What’s the ongoing story: US President Donald Trump may have hit the pause on his trade vacillations, but there seems to be a lingering deleterious effect on the American Dollar, which has slumped sharply. Reason: waning confidence in the American economy is leading to a huge flight out of the greenback to other safe haven currencies and gold.
Key Points to Ponder:
— What is the volatility index?
— What is bond yield?
— What is the dollar index?
— What is its impact on the Indian Rupee?
— What is the impact of a sudden change in government policies on the bond yield?
— Trump’s “reciprocal tariffs” neither address inflation nor the dollar’s overvaluation. Evaluate.
Key Takeaways:
— The US economy has dominated the global order for the past eight decades because not only is it the biggest economy — its GDP is close to $30 trillion — it is also the most well-regulated and freely traded economy. Its currency is managed very professionally and the executive branch (the US President) cannot interfere in monetary policy.
— In other countries, including India and China, the government has a much greater say on monetary policy and this erodes the confidence an random investor has in the value of the currency.
— However, with his adamance to place prohibitive tariffs against all the countries in the world, President Trump has dialled back time to an era when the US was not the standard-bearer of the world. The worst part of Trump’s policy is the uncertainty that it has infused about his own policy stance. There is no clarity what his end goal is when he levies the tariffs, or how he calculates the tariff rates.
— Trump’s sudden climbdown on reciprocal tariffs is said to have been triggered by the selloff in American bonds, as confidence in the US economy plummeted and bond holders waned. Foreign holders, including Japanese and Chinese investors, are among those said to have dumped US government debt amid spiralling concerns over the impact of Trump’s tariffs.
— US President Donald Trump’s unilateral tariff impositions — 10% (at present) on goods imported from most countries and 145% from China — are comparable, for the scale of shocks unleashed and transformation engendered to the international trading or monetary system, to two other actions initiated by powerful men.
— The first was by a former president and the second by a central banker, both also from the US. Read more
Do You Know:
— The bond market refers to the marketplace where a government (and even corporates/ companies) go to borrow money. It is different from the stock market where investors buy a piece of a company by owning a share of it.
— Governments are the biggest borrowers because they have to meet the gap between their revenues and expenditures. And because governments are not expected to default, when a government floats a bond — a paper which says the government owes the bearer of that paper a particular sum at the end of a year or 10 years — it is considered to be the safest asset in any economy.
— Holding a government bond is in practical terms as good as holding cash and the effective return (called the yield) that one earns from a government bond is considered to be the risk-free return in that economy.
— That is why the effective interest rate (yield) earned on a government bond changes over time as the price of the bond itself changes. This essentially means that if the bond prices fall, the yield rises and vice-versa.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Trump’s tariffs and a tale of three human-made global shocks
📍Dollar slumps as US faces loss of confidence – impact on Indian rupee, other currencies
UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
(6) The problem of International liquidity is related to the non-availability of (2015)
(a) goods and services
(b) gold and silver
(c) dollars and other hard currencies
(d) exportable surplus
|
ALSO IN NEWS |
|
| India natural economic partner, key to stability in Indo-Pacific region, says Italian Deputy PM Antonio Tajani | External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar met Italy’s visiting Deputy PM Antonio Tajani and they reviewed bilateral cooperation in a range of areas, including defence, trade and investment and energy. |
| Instagram is making us buy our belongingness | Another product, another promise, another glimpse into a life just slightly out of reach. And we, the consumers, remain caught between aspiration and reality — buying things we don’t need, to impress people we don’t even like. |
| PRELIMS ANSWER KEY |
| 1. (c) 2. (c) 3. (d) 4. (b) 5. (b) 6. (c) |
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter. Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – IndianExpress UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.
🚨 Click Here to read the UPSC Essentials magazine for March 2025. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨
Must Read
Buzzing Now
May 24: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05



























